Services List
-
Services By Handling Problems

Transfer Chute Design
Transfer chutes are used in bulk handling systems to perform a variety of operations. For instance accelerating the bulk material from a slow moving belt or apron feeder onto a conveyor, or capturing and re-directing the flow of bulk material from one conveyor belt to another.
It is important that a chute is designed correctly to ensure the efficient transfer of bulk solids without spillage and blockages and with minimum chute and belt wear. The importance is accentuated with a trend towards higher conveying speeds and ever increasing throughputs.
The transfer chute design services offered by our team of specialist engineers at TUNRA Bulk Solids (TBS) include troubleshooting, design audits, wear liner selection and development of concept designs and technical specification criteria.
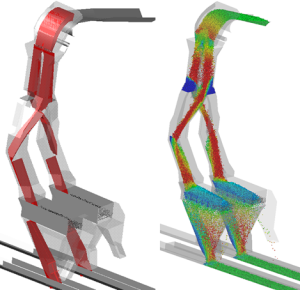
Troubleshooting, Design Audit and Concept Design Capabilities:
- Greenfield 3D concept design (geometry and position of transfer chute for optimum flow)
- Brownfield 3D re-design (concept design and minimised flow problems with a set of imposed structural/geometrical constraints already in place)
- Independent assessment of proposed designs and compliance to technical design specification criteria
- Evaluation of transfer design including discharge trajectories, hood and spoon type accelerated flow systems, bifurcated systems (including flop gate), slewing/luffing stacker reclaimers, rock box or dead box (internal shear type) and spreader/diverter type systems
- Evaluation and selection of most suitable wall (friction) and wear (longevity) lining materials
- Mathematical analysis based on material flow property testing results using Continuum Mechanics
- Modelling material trajectory and material stream flow including velocity and cross sectional area profile
- Discrete Element Modelling (DEM) 3D flow simulation – based on input parameters calibrated from material flow property testing results and project/application specific calibration tests
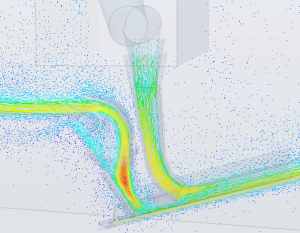
TUNRA Transfer Chute Design Principles for Optimum Flow:
- Selection of most favourable wall lining material based on flow property testing results – lowest friction, highest wear resistance
- Selection of transfer head height and geometry related to satisfying operational criteria
- Minimising impact angles between flowing/discharging material stream and transfer chute geometry
- Centralised flow for minimising chance of belt mis-tracking problems and spillage
- Sufficient chute cut-off angles (slope) to guarantee flow at specified rate under all conditions, minimising flow retardation and preventing blockage
- Matching as close as possible inline component of bulk solid material stream velocity at exit of the chute and loading to the velocity of outgoing conveyor belt
- Minimising normal component of bulk solid material stream velocity at loading point thereby reducing impact wear on the belt
Case Studies
The following case studies highlight a selection of transfer chute design projects completed by TBS:
-
Services By Industry

Transfer Chute Design
Transfer chutes are used in bulk handling systems to perform a variety of operations. For instance accelerating the bulk material from a slow moving belt or apron feeder onto a conveyor, or capturing and re-directing the flow of bulk material from one conveyor belt to another.
It is important that a chute is designed correctly to ensure the efficient transfer of bulk solids without spillage and blockages and with minimum chute and belt wear. The importance is accentuated with a trend towards higher conveying speeds and ever increasing throughputs.
The transfer chute design services offered by our team of specialist engineers at TUNRA Bulk Solids (TBS) include troubleshooting, design audits, wear liner selection and development of concept designs and technical specification criteria.

Troubleshooting, Design Audit and Concept Design Capabilities:
- Greenfield 3D concept design (geometry and position of transfer chute for optimum flow)
- Brownfield 3D re-design (concept design and minimised flow problems with a set of imposed structural/geometrical constraints already in place)
- Independent assessment of proposed designs and compliance to technical design specification criteria
- Evaluation of transfer design including discharge trajectories, hood and spoon type accelerated flow systems, bifurcated systems (including flop gate), slewing/luffing stacker reclaimers, rock box or dead box (internal shear type) and spreader/diverter type systems
- Evaluation and selection of most suitable wall (friction) and wear (longevity) lining materials
- Mathematical analysis based on material flow property testing results using Continuum Mechanics
- Modelling material trajectory and material stream flow including velocity and cross sectional area profile
- Discrete Element Modelling (DEM) 3D flow simulation – based on input parameters calibrated from material flow property testing results and project/application specific calibration tests

TUNRA Transfer Chute Design Principles for Optimum Flow:
- Selection of most favourable wall lining material based on flow property testing results – lowest friction, highest wear resistance
- Selection of transfer head height and geometry related to satisfying operational criteria
- Minimising impact angles between flowing/discharging material stream and transfer chute geometry
- Centralised flow for minimising chance of belt mis-tracking problems and spillage
- Sufficient chute cut-off angles (slope) to guarantee flow at specified rate under all conditions, minimising flow retardation and preventing blockage
- Matching as close as possible inline component of bulk solid material stream velocity at exit of the chute and loading to the velocity of outgoing conveyor belt
- Minimising normal component of bulk solid material stream velocity at loading point thereby reducing impact wear on the belt
Case Studies
The following case studies highlight a selection of transfer chute design projects completed by TBS:
-
Services By Material Type

Transfer Chute Design
Transfer chutes are used in bulk handling systems to perform a variety of operations. For instance accelerating the bulk material from a slow moving belt or apron feeder onto a conveyor, or capturing and re-directing the flow of bulk material from one conveyor belt to another.
It is important that a chute is designed correctly to ensure the efficient transfer of bulk solids without spillage and blockages and with minimum chute and belt wear. The importance is accentuated with a trend towards higher conveying speeds and ever increasing throughputs.
The transfer chute design services offered by our team of specialist engineers at TUNRA Bulk Solids (TBS) include troubleshooting, design audits, wear liner selection and development of concept designs and technical specification criteria.

Troubleshooting, Design Audit and Concept Design Capabilities:
- Greenfield 3D concept design (geometry and position of transfer chute for optimum flow)
- Brownfield 3D re-design (concept design and minimised flow problems with a set of imposed structural/geometrical constraints already in place)
- Independent assessment of proposed designs and compliance to technical design specification criteria
- Evaluation of transfer design including discharge trajectories, hood and spoon type accelerated flow systems, bifurcated systems (including flop gate), slewing/luffing stacker reclaimers, rock box or dead box (internal shear type) and spreader/diverter type systems
- Evaluation and selection of most suitable wall (friction) and wear (longevity) lining materials
- Mathematical analysis based on material flow property testing results using Continuum Mechanics
- Modelling material trajectory and material stream flow including velocity and cross sectional area profile
- Discrete Element Modelling (DEM) 3D flow simulation – based on input parameters calibrated from material flow property testing results and project/application specific calibration tests

TUNRA Transfer Chute Design Principles for Optimum Flow:
- Selection of most favourable wall lining material based on flow property testing results – lowest friction, highest wear resistance
- Selection of transfer head height and geometry related to satisfying operational criteria
- Minimising impact angles between flowing/discharging material stream and transfer chute geometry
- Centralised flow for minimising chance of belt mis-tracking problems and spillage
- Sufficient chute cut-off angles (slope) to guarantee flow at specified rate under all conditions, minimising flow retardation and preventing blockage
- Matching as close as possible inline component of bulk solid material stream velocity at exit of the chute and loading to the velocity of outgoing conveyor belt
- Minimising normal component of bulk solid material stream velocity at loading point thereby reducing impact wear on the belt
Case Studies
The following case studies highlight a selection of transfer chute design projects completed by TBS:











